Glossary
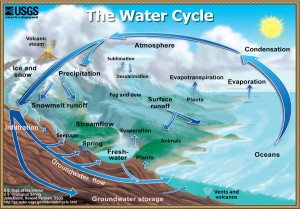
Terms and definitions relating to watersheds and the hydrologic (water) cycle
Have you ever wondered what NON-POTABLE means? How about RAIN SHADOW? Take a look at these words and see how many you know…you may be surprised.
Ahupuaʻa: the Hawaiian equivalent of a watershed; a strip of land, usually between two ridges, that reaches from summit to sea
Aquifer: water bearing rock
Ahupuaʻa: the Hawaiian equivalent of a watershed; a strip of land, usually between two ridges, that reaches from summit to sea
Aquifer: water bearing rock
Artesian well: a well drilled through impermeable strata to reach water; pushed by pressure from the underground aquifer, this water naturally rises to the earth’s surface
Boiling point: the temperature at which a liquid boils; for water this is 212 degrees Fahrenheit (100 degrees Celsius)
Desalination: removal of salt from seawater using a semi-permeable membrane; the membrane prevents the passage of salts as the water is forced through it
Dew: water vapor that condenses on sold surfaces that have cooled below the condensation point of water
Dew point: temperature at which water vapor condenses into cloud droplets
Dike: underground water barrier formed of nonporous, dense volcanic bedrock (basalt); can form water storage chambers

Erosion: the process by which soils loosen from the earth due to exposure to the elements; this topsoil eventually washes into the ocean, polluting the sea
Evaporation: conversion of liquid water through heat energy into water vapor
Fog drip: water vapor which condenses on cooler surfaces such as rocks and plants without falling to earth as rain
Ghyben-Herzberg lens: freshwater aquifer below a tropical ocean island; rainwater percolates through the island and floats above the surrounding seawater; this groundwater forms a root shape beneath the island, usually 40 times as thick as below sea level as above.
Groundwater: any water beneath the earth’s surface; or a region of subsurface water that forms a saturation zone in which all pore spaces are filled with water
Hydrologic: concerning water on the earth’s surface, in the soil and underlying rocks and in the atmosphere
Intermittent stream: surface water that flows seasonally or only after heavy storms
Non-potable: lower quality water with high mineral content; safe for occasional inadvertent human consumption, conforms to state and federal requirements for this level
Orographic lifting: winds push moist air up against mountains or cliffs to produce clouds and precipitation
Percolation: rainwater slowly sinks through the island’s soil and porous volcanic rock; passage of a raindrop from mountain top to aquifer takes roughly 25 years.
Perched water: smaller volumes of groundwater trapped between layers of porous and less porous material
Perennial stream: permanently flowing water, fed by consistent rainfall
Porous: having small pores or holes through which materials such as water can pass
Potable: drinkable water of excellent quality, conforms to state and federal requirements
Precipitation: rain, snow, dew, frost, sleet, or hail condensed from atmospheric water vapor (clouds) and falling to earth
Pump: in relation to a forested watershed with cool and cloudy conditions, plants act as a pump to put water back into the soil
Rain shadow: area sheltered from prevailing winds and rain by adjacent high ground or mountains and hence an area of low rainfall
Soil anchor: roots of trees and plants serve as an anchor to hold soils in place and prevent erosion
Sponge: the soil, roots, mosses, ferns and leaves of a forested watershed act as a sponge that soaks up precipitation. When the sponge is fully saturated, it slowly releases water into underground water tables and streams
Spring: water that emerges from an underground source to feed streams or release freshwater directly into the ocean
Surface water: water flowing or collecting at the level of the earth’s surface, such as streams, rivers, springs, or lakes
Transpiration: evaporation of water from the surface of a plant
Umbrella: Trees and plants serve as an umbrella to intercept rain and wind, thus reducing the erosive capacity of precipitation and storms
Water table: level under the ground in permeable or porous rock below which the ground is completely saturated with water